Kinematics Class Reference
Forward and inverse kinematics calculations using Tekkotsu output indices. More...
#include <Kinematics.h>
Detailed Description
Forward and inverse kinematics calculations using Tekkotsu output indices.
You should read the Kinematics tutorial to get a general understanding of the math involved and diagrams for usage with supported robots.
This class involves all aspects of the forward kinematics: calculations concerning locations and orientations in space given a known set of joint configurations. There is a global instantiation of Kinematics named kine, which can be used to perform these calculations regarding the joint positions currently in state.
To perform kinematics on a hypothetical set of joint values, use PostureEngine or one of its subclasses. PostureEngine also adds inverse kinematic functions, which will allow you to determine joint angles in order to reach a given point.
Wherever a reference frame index is requested, you can simply supply one of the output indexes in the usual manner:
However, there are also a number of points on the body which are not joints, but should have their own reference frames, such as the base frame, or the camera. These frames have their own indices, listed in the robot info file for the model in question (such as ERS7Info.h), with names ending in FrameOffset.
Example code:
// Find the ray from the camera to whatever the near-field IR is hitting: fmat::Transform T = kine->linkToLink(NearIRFrameOffset,CameraFrameOffset); fmat::Column<3> camera_ray = T*fmat::pack(0,0,state->sensors[NearIRDistOffset]); float x; // x will be in the range ±1 for resolution layer independence float y; // y ranges ±y_dim/x_dim (i.e. ±1/aspectRatio) config->vision.computePixel(camera_ray[0],camera_ray[1],camera_ray[2],x,y);
Finally, for each model we have created a database of "interest points" -- locations of notable interest on the body of the robot. These may be of use to people attempting to use the limbs to manipulate objects. To access these interest points, call getInterestPoint with the name of the interest point, obtained from the diagrams.
Note that you can pass a comma separated list of interest point names and the result will be the midpoint of those interest points:
kine->getInterestPoint(BaseFrameOffset,"LowerInnerFrontLFrShin,LowerOuterFrontLFrShin");
- See also:
- PostureEngine for inverse kinematics
Definition at line 68 of file Kinematics.h.
Classes | |
| struct | InterestPoint |
| holds the position and attached link of a given interest point More... | |
Public Member Functions | |
| Kinematics () | |
| Constructor, pass the full path to the kinematics configuration file. | |
| Kinematics (const Kinematics &k) | |
| Copy constructor, everything is either update-before-use or static, copy is normal init. | |
| Kinematics & | operator= (const Kinematics &k) |
| Assignment operator, everything is either update-before-use or static, assignment is no-op. | |
| virtual | ~Kinematics () |
| Destructor. | |
| const KinematicJoint * | getRoot () |
| Returns a pointer to the root of the kinematic tree. | |
| const KinematicJoint * | getKinematicJoint (unsigned int idx) const |
| returns the KinematicJoint structure for the specified Tekkotsu output or reference frame offset | |
| fmat::Column< 3 > | getPosition (unsigned int idx) const |
| fmat::Transform | linkToBase (unsigned int link) |
| Returns a matrix for transforming from link frame j to base frame. | |
| fmat::Transform | baseToLink (unsigned int link) |
| Returns a matrix for transforming from the base frame to link j frame. | |
| fmat::Transform | linkToLink (unsigned int iL, unsigned int oL) |
| Returns a matrix for transforming from link iL to link oL. | |
| fmat::Transform | baseToLocal () |
| returns a transformation to account for standing pose, where the origin of the "local" space is the projection of the base frame origin along the ground plane normal | |
| fmat::Transform | baseToLocal (const PlaneEquation &plane) |
| returns a transformation to account for standing pose, where the origin of the "local" space is the projection of the base frame origin along the ground plane normal | |
| fmat::Transform | localToBase () |
| returns a transformation to account for standing pose, where the origin of the "local" space is the projection of the base frame origin along the ground plane normal | |
| fmat::Transform | localToBase (const PlaneEquation &plane) |
| returns a transformation to account for standing pose, where the origin of the "local" space is the projection of the base frame origin along the ground plane normal | |
| void | getInterestPoint (const std::string &name, unsigned int &link, fmat::Column< 3 > &ip, bool convertToJoint=false) |
| Returns the location of a named point and the link it is attached to. | |
| fmat::Column< 3 > | getInterestPoint (unsigned int link, const std::string &name) |
| Returns the location of a named point, relative to any desired reference frame. | |
| void | calcLegHeights (const fmat::Column< 3 > &down, float heights[NumLegs]) |
| Calculate the leg heights along a given "down" vector (0 is level with base frame). | |
| LegOrder_t | findUnusedLeg (const fmat::Column< 3 > &down) |
| Find the leg which is in least contact with ground. | |
| PlaneEquation | calculateGroundPlane () |
| Find the ground plane by fitting a plane to the lowest 3 interest points. | |
| PlaneEquation | calculateGroundPlane (const fmat::Column< 3 > &down) |
| Find the ground plane by fitting a plane to the lowest 3 interest points. | |
| fmat::Column< 4 > | projectToPlane (unsigned int j, const fmat::Column< 3 > &r_j, unsigned int b, const PlaneEquation &p_b, unsigned int f, float objCentroidHeight=0) |
| Find the point of intersection between a ray and a plane. | |
| fmat::Column< 4 > | projectToGround (unsigned int j, const fmat::Column< 3 > &r_j, float objCentroidHeight=0) |
| Find the location of an object on the ground from an arbitrary ray r_j in reference frame j (probably CameraFrameOffset). | |
| fmat::Column< 4 > | projectToGround (const VisionObjectEvent &visObj, float objCentroidHeight=0) |
| Find the location of an object on the ground (the easy way from a vision object event (i.e. EventBase::visObjEGID)). | |
| fmat::Column< 4 > | projectToGround (const VisionObjectEvent &visObj, const PlaneEquation &gndPlane, float objCentroidHeight=0) |
| Find the location of an object on the ground with a custom ground plane specification. | |
| virtual void | update () const |
| refresh the joint settings in root from WorldState::outputs | |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static fmat::Column< 3 > | pack (float x, float y, float z) |
| A simple utility function, converts x,y,z,h to a fmat::Column<3> | |
| static fmat::Column< 4 > | pack (float x, float y, float z, float h) |
| A simple utility function, converts x,y,z,h to a fmat::Column<4> | |
| static void | unpack (const fmat::SubVector< 4, const float > &m, float &ox, float &oy, float &oz) |
| A simple utility function, pulls the first 3 rows of the first column, divides each by the fourth row, and stores into ox, oy, and oz. | |
Protected Types | |
| typedef std::map< std::string, InterestPoint > | InterestPointMap |
| we'll be using the hash_map to store named interest points | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| void | init () |
| Called by constructors to do basic setup - first call will read Config::motion_config::kinematics from disk, future initializes reuse static roconfig. | |
Static Protected Member Functions | |
| static void | initStatics () |
| initializes static variables -- only call if not staticsInited | |
| static void | checkStatics () |
| checks that statics have been initialized, and calls initStatics if they are missing | |
Protected Attributes | |
| KinematicJoint | root |
| the root of the kinematic tree | |
| unsigned int | lastUpdateTime |
| determine if the joints are up to date (compare to WorldState::lastSensorUpdateTime) | |
| KinematicJoint * | jointMaps [NumReferenceFrames] |
| holds mapping from tekkotsu output index to chain and link indicies | |
Static Protected Attributes | |
| static bool | staticsInited = false |
| initially false, set to true after first Kinematics is initialized | |
| static InterestPointMap | ips |
| these interest points are shared by all Kinematics classes (i.e. all PostureEngines) | |
Member Typedef Documentation
typedef std::map<std::string,InterestPoint> Kinematics::InterestPointMap [protected] |
we'll be using the hash_map to store named interest points
Definition at line 290 of file Kinematics.h.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
| Kinematics::Kinematics | ( | ) |
Constructor, pass the full path to the kinematics configuration file.
Definition at line 71 of file Kinematics.h.
| Kinematics::Kinematics | ( | const Kinematics & | k | ) |
Copy constructor, everything is either update-before-use or static, copy is normal init.
Definition at line 76 of file Kinematics.h.
| Kinematics::~Kinematics | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Destructor.
Definition at line 40 of file Kinematics.cc.
Member Function Documentation
| fmat::Transform Kinematics::baseToLink | ( | unsigned int | link | ) |
Returns a matrix for transforming from the base frame to link j frame.
- Parameters:
-
[in] link the output offset, see class notes for values
Definition at line 118 of file Kinematics.h.
Referenced by RawCam::drawShapesIntoBuffer(), projectShapeToCamera(), and PostureEngine::solveLinkVector().
| fmat::Transform Kinematics::baseToLocal | ( | const PlaneEquation & | plane | ) |
returns a transformation to account for standing pose, where the origin of the "local" space is the projection of the base frame origin along the ground plane normal
Definition at line 44 of file Kinematics.cc.
| fmat::Transform Kinematics::baseToLocal | ( | ) |
returns a transformation to account for standing pose, where the origin of the "local" space is the projection of the base frame origin along the ground plane normal
Definition at line 131 of file Kinematics.h.
Referenced by baseToLocal(), Grasper::ReleaseArm::doStart(), and localToBase().
| void Kinematics::calcLegHeights | ( | const fmat::Column< 3 > & | down, | |
| float | heights[NumLegs] | |||
| ) |
Calculate the leg heights along a given "down" vector (0 is level with base frame).
This can be based on either the gravity vector from accelerometer readings, or if that may be unreliable due to being in motion, you could do some basic balance modeling and pass a predicted vector. This uses the interest point database to find the lowest interest point for each leg
- Note:
- on Aibo platforms, if packing accelerometer readings, don't forget to negate the "left" accelerometer!
Definition at line 115 of file Kinematics.cc.
Referenced by findUnusedLeg().
| PlaneEquation Kinematics::calculateGroundPlane | ( | const fmat::Column< 3 > & | down | ) |
Find the ground plane by fitting a plane to the lowest 3 interest points.
- Note:
- on Aibo platforms, if packing accelerometer readings, don't forget to negate the "left" accelerometer!
- Returns:
- vector of the form
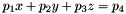 , relative to the base frame
, relative to the base frame
Definition at line 173 of file Kinematics.cc.
| PlaneEquation Kinematics::calculateGroundPlane | ( | ) |
Find the ground plane by fitting a plane to the lowest 3 interest points.
This function merely calls the other version of calculateGroundPlane with the current gravity vector as the "down" vector.
- Returns:
- vector of the form
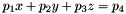 , relative to the base frame
, relative to the base frame
Definition at line 159 of file Kinematics.cc.
Referenced by baseToLocal(), DualCoding::MapBuilder::calculateGroundPlane(), LookAtMarkers::Search::doEvent(), LookAtMarkers::TrackMarker::doEvent(), localToBase(), DualCoding::Lookout::processSearchEvent(), projectToGround(), DualCoding::MapBuilder::projectToLocal(), and DualCoding::Lookout::setupTrack().
| static void Kinematics::checkStatics | ( | ) | [static, protected] |
checks that statics have been initialized, and calls initStatics if they are missing
Definition at line 261 of file Kinematics.h.
Referenced by init().
| LegOrder_t Kinematics::findUnusedLeg | ( | const fmat::Column< 3 > & | down | ) |
Find the leg which is in least contact with ground.
- See also:
- calcLegHeights()
- Note:
- on Aibo platforms, if packing accelerometer readings, don't forget to negate the "left" accelerometer!
- Returns:
- index of leg which is highest in reference to gravity vector
Definition at line 147 of file Kinematics.cc.
| fmat::Column< 3 > Kinematics::getInterestPoint | ( | unsigned int | link, | |
| const std::string & | name | |||
| ) |
Returns the location of a named point, relative to any desired reference frame.
- Parameters:
-
[in] link the desired link reference frame to give results in [in] name the name of the interest point; varies by model, see the diagrams for your model.
You can pass a comma separated list of interest point names and the result will be the midpoint of those IPs.
If an interest point is not found, a std::runtime_error is thrown.
Definition at line 89 of file Kinematics.cc.
| void Kinematics::getInterestPoint | ( | const std::string & | name, | |
| unsigned int & | link, | |||
| fmat::Column< 3 > & | ip, | |||
| bool | convertToJoint = false | |||
| ) |
Returns the location of a named point and the link it is attached to.
- Parameters:
-
[in] name the name of the interest point; varies by model, see the diagrams for your model. [out] link on exit, offset of the link, or -1U if not found [out] ip on exit, the requested point, relative to the link frame returned in link [in] convertToJoint if true and name is relative to a "pure" reference frame (i.e. NumOutputs <= link < NumReferenceFrames), then link and ip will be transformed to the parent joint (if it exists)
If name is not found, link will be -1 and ip will be all 0's.
Definition at line 67 of file Kinematics.cc.
Referenced by getInterestPoint().
| const KinematicJoint* Kinematics::getKinematicJoint | ( | unsigned int | idx | ) | const |
returns the KinematicJoint structure for the specified Tekkotsu output or reference frame offset
Definition at line 98 of file Kinematics.h.
Referenced by ArmController::ArmController(), CBracketGrasperPredicate< N >::CBracketGrasperPredicate(), RRTNode3DR< N >::CollisionChecker::CollisionChecker(), RRTNode2DR< N >::CollisionChecker::CollisionChecker(), Grasper::computeGoalStates(), XWalkParameters::computeNeutralPos(), Grasper::PlanArmApproach::doStart(), ArmController::doStart(), Grasper::MoveArm::executeMove(), Grasper::getCurrentState(), IKCalliope::IKCalliope(), HeadPointerMC::lookAtPoint(), HeadPointerMC::lookInDirection(), ArmMC::moveOffsetToPoint(), ArmMC::moveOffsetToPointWithOrientation(), ArmController::setJoint(), ShapeSpaceCollisionCheckerBase< N >::ShapeSpaceCollisionCheckerBase(), ShapeSpacePlanner2DR< N >::ShapeSpacePlanner2DR(), and ShapeSpacePlanner3DR< N >::ShapeSpacePlanner3DR().
| fmat::Column<3> Kinematics::getPosition | ( | unsigned int | idx | ) | const |
Definition at line 100 of file Kinematics.h.
Referenced by Grasper::PlanBodyTransport::doStart(), Grasper::ArmRaise::doStart(), Grasper::ArmNudge::doStart(), Grasper::PlanArmApproach::doStart(), Grasper::PlanBodyApproach::doStart(), ArmController::pointPicked(), and ArmMC::setFingerGap().
| const KinematicJoint* Kinematics::getRoot | ( | ) |
Returns a pointer to the root of the kinematic tree.
Definition at line 95 of file Kinematics.h.
| void Kinematics::init | ( | ) | [protected] |
Called by constructors to do basic setup - first call will read Config::motion_config::kinematics from disk, future initializes reuse static roconfig.
Reimplemented in PostureMC.
Definition at line 23 of file Kinematics.cc.
Referenced by Kinematics().
| void Kinematics::initStatics | ( | ) | [static, protected] |
initializes static variables -- only call if not staticsInited
Definition at line 34 of file Kinematics.cc.
Referenced by checkStatics().
| fmat::Transform Kinematics::linkToBase | ( | unsigned int | link | ) |
Returns a matrix for transforming from link frame j to base frame.
- Parameters:
-
[in] link the output offset, see class notes for values
Definition at line 109 of file Kinematics.h.
Referenced by baseToLink(), LookAtMarkers::Search::doEvent(), LookAtMarkers::TrackMarker::doEvent(), KoduInterpreter::GiveActionRunner::GiveActionSend::doStart(), KoduInterpreter::GrabActionRunner::ExecuteGrabAction::PrepareForAnotherGrasp::RepositionBody::doStart(), KoduInterpreter::GrabActionRunner::ExecuteGrabAction::VerifyObjectWasGrabbed::VerifyObjectInGripper::doStart(), KoduInterpreter::GrabActionRunner::ExecuteGrabAction::VerifyObjectWasGrabbed::LookAtTheGripper::doStart(), KoduInterpreter::PerceptualMultiplexor::FailureRecovery::ObjectManipRecovery::PrepareForAnotherGrasp::RepositionBody::doStart(), KoduInterpreter::PerceptualMultiplexor::FailureRecovery::ObjectManipRecovery::VerifyObjectWasGrabbed::VerifyObjectInGripper::doStart(), KoduInterpreter::PerceptualMultiplexor::FailureRecovery::ObjectManipRecovery::VerifyObjectWasGrabbed::LookAtTheGripper::doStart(), Grasper::ReleaseArm::doStart(), Grasper::Verify::CheckCross::doStart(), Grasper::Verify::CheckDomino::doStart(), Grasper::DoBodyApproach3::doStart(), Grasper::DoBodyApproach2::doStart(), DualCoding::Lookout::findLocationFor(), DualCoding::MapBuilder::getCamCrosses(), DualCoding::MapBuilder::getCamCylinders(), DualCoding::MapBuilder::getCamDominoes(), DualCoding::MapBuilder::grabCameraImageAndGo(), HeadPointerMC::lookAtJoint(), DualCoding::Lookout::processPointAtEvent(), DualCoding::Lookout::processSearchEvent(), DualCoding::MapBuilder::projectToLocal(), and DualCoding::Lookout::setupTrack().
| fmat::Transform Kinematics::linkToLink | ( | unsigned int | iL, | |
| unsigned int | oL | |||
| ) |
Returns a matrix for transforming from link iL to link oL.
- Parameters:
-
[in] iL the output offset to convert from, see class notes for values [in] oL the output offset to convert to, see class notes for values
Definition at line 123 of file Kinematics.h.
Referenced by getInterestPoint(), IKCalliope::IKCalliope(), and ArmMC::setFingerGap().
| fmat::Transform Kinematics::localToBase | ( | const PlaneEquation & | plane | ) |
returns a transformation to account for standing pose, where the origin of the "local" space is the projection of the base frame origin along the ground plane normal
Definition at line 140 of file Kinematics.h.
Referenced by localToBase().
| fmat::Transform Kinematics::localToBase | ( | ) |
returns a transformation to account for standing pose, where the origin of the "local" space is the projection of the base frame origin along the ground plane normal
Definition at line 137 of file Kinematics.h.
| Kinematics& Kinematics::operator= | ( | const Kinematics & | k | ) |
Assignment operator, everything is either update-before-use or static, assignment is no-op.
Definition at line 83 of file Kinematics.h.
| static fmat::Column<4> Kinematics::pack | ( | float | x, | |
| float | y, | |||
| float | z, | |||
| float | h | |||
| ) | [static] |
A simple utility function, converts x,y,z,h to a fmat::Column<4>
- Parameters:
-
[in] x the value for the first element [in] y the value for the second element [in] z the value for the third element [in] h the value for the fourth element
- Returns:
![$ \left[\begin{array}{c} x\\y\\z\\h\\ \end{array}\right] $](form_7.png)
Definition at line 242 of file Kinematics.h.
| static fmat::Column<3> Kinematics::pack | ( | float | x, | |
| float | y, | |||
| float | z | |||
| ) | [static] |
A simple utility function, converts x,y,z,h to a fmat::Column<3>
- Parameters:
-
[in] x the value for the first element [in] y the value for the second element [in] z the value for the third element
- Returns:
![$ \left[\begin{array}{c} x\\y\\z\\ \end{array}\right] $](form_6.png)
Definition at line 234 of file Kinematics.h.
Referenced by calculateGroundPlane(), getInterestPoint(), DualCoding::Lookout::moveHeadToPoint(), pack(), projectToPlane(), and PostureEngine::solveLinkVector().
| fmat::Column< 4 > Kinematics::projectToGround | ( | const VisionObjectEvent & | visObj, | |
| const PlaneEquation & | gndPlane, | |||
| float | objCentroidHeight = 0 | |||
| ) |
Find the location of an object on the ground with a custom ground plane specification.
gndPlane must be specified relative to the base frame, in the form 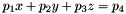 ,
,
- See also:
- projectToPlane() for more control over projection and results
Definition at line 542 of file Kinematics.cc.
| fmat::Column<4> Kinematics::projectToGround | ( | const VisionObjectEvent & | visObj, | |
| float | objCentroidHeight = 0 | |||
| ) |
Find the location of an object on the ground (the easy way from a vision object event (i.e. EventBase::visObjEGID)).
- Parameters:
-
visObj the vision object to project objCentroidHeight the height of the object's centroid above the ground Uses the default calculateGroundPlane(), otherwise call the other projectToGround() to specify a custom plane.
Definition at line 219 of file Kinematics.h.
| fmat::Column<4> Kinematics::projectToGround | ( | unsigned int | j, | |
| const fmat::Column< 3 > & | r_j, | |||
| float | objCentroidHeight = 0 | |||
| ) |
Find the location of an object on the ground from an arbitrary ray r_j in reference frame j (probably CameraFrameOffset).
- Parameters:
-
visObj the vision object to project objCentroidHeight the height of the object's centroid above the ground Uses the default calculateGroundPlane(), otherwise call projectToPlane() to specify a custom plane.
Definition at line 211 of file Kinematics.h.
Referenced by projectToGround().
| fmat::Column< 4 > Kinematics::projectToPlane | ( | unsigned int | j, | |
| const fmat::Column< 3 > & | r_j, | |||
| unsigned int | b, | |||
| const PlaneEquation & | p_b, | |||
| unsigned int | f, | |||
| float | objCentroidHeight = 0 | |||
| ) |
Find the point of intersection between a ray and a plane.
- Parameters:
-
j is the link number the ray is relative to r_j is the ray through the origin of link j b is the link number the plane is relative to (probably BaseFrameOffset) p_b represents the plane to be intersected f is the link number the results should be relative to objCentroidHeight the height of the object's centroid above the ground
p_b should be of the form 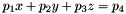
- Returns:
- homogeneous coordinate of intersection (may be infinity)
For projecting to the ground plane, one of the specialized projectToGround() functions may be more convenient.
Mathematical implementation:
We'll convert the ray to the plane's reference frame, solve there. We find a point on the ray (ro_b) and the direction of the ray (rv_b). rv_b does not need to be normalized because we're going to find a scaling factor for it, and that factor accounts for current magnitude.
Proof, p=plane normal vector, d=plane displacement, r = ray direction, o = ray offset, x = [x y z] coordinates, t = scaling factor

Find distance from the ray offset (ro_b) and the closest point on the plane.
Object height is applied along the plane normal toward the ray origin (we assume the ray source is "above" ground)
Find scaling factor by projecting ray vector (rv_b) onto plane normal.
Intersection point will be rv_b*dist/align + ro_b, but need to watch out for case where align==0 (rv_b and plane are parallel, no intersection)
Definition at line 468 of file Kinematics.cc.
Referenced by projectToGround().
| static void Kinematics::unpack | ( | const fmat::SubVector< 4, const float > & | m, | |
| float & | ox, | |||
| float & | oy, | |||
| float & | oz | |||
| ) | [static] |
A simple utility function, pulls the first 3 rows of the first column, divides each by the fourth row, and stores into ox, oy, and oz.
- Parameters:
-
[in] m the column to unpack from, applying scaling factor [out] ox set to the first element of m, divided by fourth element [out] oy set to the second element of m, divided by fourth element [out] oz set to the third row element of m, divided by fourth element
Definition at line 249 of file Kinematics.h.
| void Kinematics::update | ( | ) | const [virtual] |
refresh the joint settings in root from WorldState::outputs
Reimplemented in PostureEngine.
Definition at line 554 of file Kinematics.cc.
Referenced by calcLegHeights(), calculateGroundPlane(), getKinematicJoint(), getPosition(), linkToBase(), linkToLink(), and projectToPlane().
Member Data Documentation
Kinematics::InterestPointMap Kinematics::ips [static, protected] |
these interest points are shared by all Kinematics classes (i.e. all PostureEngines)
this is to reduce initialization time, but does mean one robot can't do interest point calculations regarding a different model robot...
Definition at line 294 of file Kinematics.h.
Referenced by calcLegHeights(), and calculateGroundPlane().
KinematicJoint* Kinematics::jointMaps[NumReferenceFrames] [protected] |
holds mapping from tekkotsu output index to chain and link indicies
Definition at line 284 of file Kinematics.h.
Referenced by calcLegHeights(), calculateGroundPlane(), getInterestPoint(), getKinematicJoint(), getPosition(), init(), Kinematics(), linkToBase(), linkToLink(), operator=(), projectToPlane(), PostureEngine::solveLink(), PostureEngine::solveLinkOrientation(), PostureEngine::solveLinkPosition(), PostureEngine::update(), and update().
unsigned int Kinematics::lastUpdateTime [mutable, protected] |
determine if the joints are up to date (compare to WorldState::lastSensorUpdateTime)
Definition at line 281 of file Kinematics.h.
Referenced by update().
KinematicJoint Kinematics::root [protected] |
the root of the kinematic tree
Definition at line 278 of file Kinematics.h.
Referenced by getRoot(), init(), Kinematics(), and operator=().
bool Kinematics::staticsInited = false [static, protected] |
initially false, set to true after first Kinematics is initialized
Definition at line 287 of file Kinematics.h.
Referenced by checkStatics(), and initStatics().
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files: